What is BPC-157 + TB-500 (Wolverine Stack)?
BPC-157 + TB-500, commonly referred to as the Wolverine stack, is a synthetic peptide blend formulated for advanced research into cellular repair, tissue regeneration, and inflammatory modulation.
The blend combines two well-studied peptides—BPC-157, derived from a protein found in gastric juice, and TB-500, a synthetic fragment of the naturally occurring Thymosin Beta-4 (TB-4) peptide.
BPC-157
BPC-157 (Body Protection Compound 157) is a 15-amino acid peptide shown in animal models to support angiogenesis, fibroblast activity, and tendon and ligament healing. It has also demonstrated protective effects in gastrointestinal and neurological injury models. Its strong stability in plasma, ease of solubility, and broad systemic activity make it a frequent subject in regenerative research.
TB-500
TB-500 is a synthetic peptide fragment designed to mimic the active region of Thymosin Beta-4, but with greater stability and shelf life, making it more practical for research storage and use. TB-500 promotes cell migration, blood vessel formation, and muscle fiber regeneration—key mechanisms in studies focused on soft tissue injury and cardiac repair.
TB-4 vs TB-500
Thymosin Beta-4 (TB-4) is a naturally occurring peptide in the human body, composed of 43 amino acids. It plays roles in cell migration, inflammation regulation, wound healing, and angiogenesis. However, full-length TB-4 is biologically fragile, expensive to synthesize, and has poor shelf stability, making it less practical for research or commercial use.
TB-500, by contrast, is a synthetic peptide fragment that mimics the key active region of Thymosin Beta-4—specifically the portion responsible for its regenerative and wound-healing effects.
| Summary: While TB-500 and TB-4 share similar biological targets, they are not identical. TB-500 is preferred in research for its longer half-life, resistance to degradation, and compatibility with BPC-157’s dosing protocols. |
Using BPC-157+ TB-500 in Research
TB-500 and BPC-157 are frequently combined in research due to their complementary dosing protocols. Both peptides are typically administered in similar cycle lengths and dosing frequencies, which simplifies their co-administration in experimental settings.
This makes a pre-formulated blend like Wolverine especially practical, allowing researchers to explore synergistic effects in tissue repair, inflammation modulation, and recovery without the complexity of managing separate compounds or mismatched schedules.
This compatibility is one reason the two peptides are often combined in preclinical models: they target overlapping but distinct pathways, with BPC-157 more focused on tendon, ligament, and gastrointestinal healing, and TB-500 on muscle regeneration and vascular growth.
When used together in research, the Wolverine blend provides a means of studying potential synergistic interactions on systemic recovery, inflammation control, and accelerated healing across multiple tissue types.
For research use only. Not for human or veterinary use. This compound is not intended for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes and has not been evaluated by regulatory agencies for safety or efficacy in humans.
Mechanism of Action (Based on Research)
The combination of BPC-157 and TB-500 has drawn interest in preclinical studies due to their complementary mechanisms in supporting tissue repair, cellular regeneration, and inflammation control.
Although these peptides are still under investigation and not approved for human use, research models suggest several potential biological roles.
Tissue Repair and Cellular Regeneration
BPC-157, a stable gastric pentadecapeptide, has been shown in animal studies to accelerate healing in muscle, tendon, and nerve tissue by enhancing angiogenesis and modulating growth factor expression. It may also influence fibroblast activity and extracellular matrix remodeling, contributing to structural tissue repair.
TB-500, a synthetic version of the naturally occurring Thymosin Beta-4 peptide fragment, appears to promote cell migration, differentiation, and wound healing by regulating actin polymerization and increasing vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) activity.
This is particularly relevant in muscle and cardiovascular research models.
Anti-Inflammatory Pathways
Both peptides have been observed to reduce pro-inflammatory cytokine levels and oxidative stress in various tissue injury models. BPC-157, in particular, has demonstrated protective effects against NSAID-induced gastric damage and may act on nitric oxide pathways to maintain vascular homeostasis.
⚠️ Disclaimer: These findings are derived from non-human studies. No therapeutic claims are made. This product is for laboratory research purposes only.
Research Applications (Wolverine Blend Benefits)
While BPC-157 and TB-500 are still under investigation and not approved for therapeutic use, preclinical studies have explored their potential in a range of biological contexts. The Wolverine blend offers researchers a practical formulation to study multi-pathway regenerative processes.
Musculoskeletal and Soft Tissue Research
Animal models have shown that BPC-157 may support the healing of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and nerves, potentially by enhancing angiogenesis, reducing inflammation, and stimulating fibroblast activity.
A study by Chang et al. (2011) investigated the effects of BPC-157 on tendon healing in rats. The researchers found that BPC-157 significantly accelerated the outgrowth of tendon fibroblasts from tendon explants. Additionally, BPC-157 enhanced cell survival under oxidative stress and increased the migration of tendon fibroblasts in a dose-dependent manner.
TB-500 complements these findings with data suggesting effects on myogenesis, muscle fiber regeneration, and wound repair, particularly through its role in actin regulation and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression.
Inflammatory Modulation
Both peptides have demonstrated anti-inflammatory activity in rodent models. BPC-157 has been observed to downregulate pro-inflammatory cytokines and protect against NSAID-induced tissue damage, while TB-500 may modulate macrophage activity and support immune cell migration.
A study by Ilic et al. (2011) examined the effects of BPC-157 on rats subjected to diclofenac-induced toxicity, which typically causes significant gastrointestinal, liver, and brain lesions. The administration of BPC-157 resulted in a marked reduction of these lesions, suggesting its protective role against NSAID-induced organ damage.
Similarly, TB-500 is a synthetic peptide fragment of Thymosin Beta-4 (TB-4), which has been associated with actin regulation and cell migration, which are crucial processes in immune response and tissue repair. TB-500 is designed to mimic these properties, and researchers often utilize it in studies focusing on wound healing and inflammation.
Post-Injury Recovery Studies
Due to overlapping properties, BPC-157 and TB-500 are frequently studied together in the context of systemic injury recovery. Research has explored their combined use in facilitating recovery following soft tissue trauma, surgery, or overuse injury, although further data is needed.
Wolverine Peptide Characteristics (BPC-157 + TB-500)
Wolverine is a research-only peptide blend combining BPC-157 and TB-500, formulated for convenience and compatibility in studies focused on tissue regeneration, inflammation modulation, and post-injury recovery.
BPC-157
- Molecular Formula: C₆₂H₉₈N₁₆O₂₂
- CAS Number: 137525-51-0
- Amino Acid Sequence: Gly-Glu-Pro-Pro-Pro-Gly-Lys-Pro-Ala-Asp-Asp-Ala-Gly-Leu-Val
- Synonyms: Body Protection Compound-157
- Molar Mass: 1,419.5355 g/mol
TB-500
- Molecular Formula: C38H68N10O14 (varies depending on manufacturing)
- CAS Number: 885340-08-9 (free base)
- Amino Acid Sequence: Ac-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro-Asp-Met-Ala-Glu-Ile-Glu-Lys-Phe-Asp-Lys-Ser-Lys-Leu-Lys-Lys-Thr-Glu-Thr-Gln-Glu-Lys-Asn-Pro-Leu-Glu-Glu-Ala-Glu-Asp-Leu-Asn-Glu-Glu-Glu-Lys-Glu-Ala-Gly-Glu-Ser
- Synonyms: Thymosin Beta-4 Fragment (TB-500)
- Molar Mass: 889.02 (may vary)
Wolverine Storage Recommendations
- Before reconstitution: Store lyophilized vials in a cool, dry place at 2–8°C (refrigerated) and away from light.
- After reconstitution: Store at 2–8°C and use within 14–28 days. Reconstitute with bacteriostatic water for best stability.
- Do not freeze after reconstitution.
This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only and is not approved for human or veterinary use.
Wolverine vs BPC-157 vs TB-500 vs Thymosin Alpha-1 Comparison
| Feature | BPC-157 + TB-500 (Wolverine) | BPC-157 Alone | TB-500 Alone | Thymosin Alpha-1 (Tα1) |
| Type | Peptide blend (regenerative peptides) | Single peptide (gut protection, tissue repair) | Single peptide (actin regulation, tissue regeneration) | Single peptide (immune modulation) |
| Primary Research Targets | Tissue repair, inflammation modulation, angiogenesis | Tissue healing, anti-inflammatory, gut protection | Wound healing, cell migration, angiogenesis | Immune response, inflammation control |
| Mechanism Complexity | Combined multi-pathway effects | Focused on fibroblast and endothelial cell activity | Focused on actin cytoskeleton and cell migration | Immune system modulation and cytokine regulation |
| Research Stage | Preclinical/early clinical research | Preclinical and some clinical studies | Preclinical research | Preclinical and clinical research |
| Observed Benefits (Preclinical Research) | Enhanced soft tissue healing and recovery, anti-inflammatory effects | Accelerated healing of muscles, tendons, ligaments | Improved wound healing, cell motility | Immune enhancement, inflammation reduction |
| Dosing Frequency | Typically cyclic, 2–4 weeks | Cyclic, usually daily or twice daily | Cyclic, similar to BPC-157 dosing | Varies, often subcutaneous injection multiple times per week |
| Approval Status | Research use only | Research use only | Research use only | Research use only / Clinical trials |
| Disclaimer | For research only, not for human use | For research only, not for human use | For research only, not for human use | For research only, not approved for human use |
Safety and Side Effects in Studies
Most research on BPC-157, TB-500, and their combination has been conducted in preclinical animal models.
To date, studies have reported minimal adverse effects at typical research-level dosages. However, it is important to note that there is insufficient data on safety or side effects in humans, and these peptides remain strictly for laboratory research purposes only.
Researchers should exercise caution and adhere to all regulatory guidelines when handling and studying these compounds.
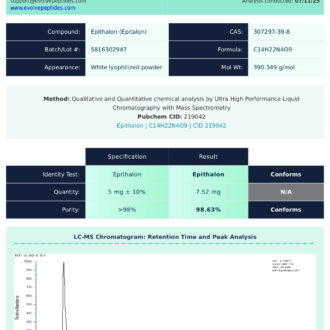
Certificate of Analysis (COA)
Evolve Peptides ensures third-party laboratory testing is performed on all peptide products, including Wolverine, to verify purity, potency, and quality. Certificates of Analysis (COAs) are available for transparency and can be provided upon request or downloaded where applicable. We are committed to supporting reliable and reproducible research outcomes.
Legal Disclaimer
This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only and is not approved for human or veterinary use. It is not for resale, diagnostic, or therapeutic applications.
Scientific References
- Józwiak, M., Bauer, M., Kamysz, W., & Kleczkowska, P. (2011). Multifunctionality and Possible Medical Application of the BPC 157 Peptide—Literature and Patent Review. Pharmaceuticals, 18(2), 185; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18020185.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21030672/ - Seiwerth, S., Milavic, M., Vukojevic, J., Gojkovic, S., Krezic, I., Batelja Vuletic, L., Horvat Pavlov, K., Petrovic, A., Sikiric, S., Vranes, H., Prtoric, A., Zizek, H., Durasin, T., Dobric, I., Staresinic, M., Strbe, S., Knezevic, M., Sola, M., Kokot, A., Sever, M., Lovric, E., Skrtic, A., Boban Blagaic, A., & Sikiric, P. (2021). Stable Gastric Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 and Wound Healing. Front Pharmacol. Jun 29;12:627533. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.627533
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21295044/ - Goldstein, A. L., Hannappel, E., Sosne, G., & Kleinman, H. K. (2012). Thymosin β4: a multi-functional regenerative peptide. Basic properties and clinical applications. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy. Jan;12(1):37-51. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2012.634793. Epub 2011 Nov 10.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5979431/ - Ilic, S., Drmic, D., Franjic, S., Kolenc, D., Coric, M., Brcic, L., Klicek, R., Radic, B., Sever, M., Djuzel, V., Filipovic, M., Djakovic, Z., Stambolija, V., Boban Blagaic, A., Zoricic, I., Gjurasin, M., Stupnisek, M., Romic, Z., Zarkovic, K., Dzidic, S., & Sikiric, P. (2011). Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 and its effects on a NSAID toxicity model: Diclofenac-induced gastrointestinal, liver, and encephalopathy lesions. Life Sciences. Volume 88, Issues 11–12, 14 March 2011, Pages 535-542
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16054264/ - Chang, C.-H., Tsai, W.-C., Lin, M.-S., Hsu, Y.-H., & Pang, J.-H. S. (2011). The promoting effect of pentadecapeptide BPC 157 on tendon healing involves tendon outgrowth, cell survival, and cell migration. Journal of Applied Physiology. Mar;110(3):774-80.
doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00945.2010. Epub 2010 Oct 28. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10385604/
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (n.d.). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 9941957, BPC-157. PubChem. Retrieved May 15, 2025, from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/BPC-157
- ChemicalBook (BPC-157 Product Page): ChemicalBook. (n.d.). BPC-157 | 137525-51-0 – Chemical Properties. Retrieved May 15, 2025, from https://www.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB34713831.htm
- MedKoo Biosciences (BPC-157 Product Page): MedKoo Biosciences. (n.d.). BPC-157 | CAS# 137525-51-0. Retrieved May 15, 2025, from https://www.medkoo.com/products/41195