Sema 2 mg
$39.00
In stock
| Quantity | Quantity | Price per Vial |
|---|---|---|
| Quantity Based Discount | 2 - 4 | 5% $37.05 |
| Quantity Based Discount | 5 - 9 | 10% $35.10 |
| Quantity Based Discount | 10 - 19 | 15% $33.15 |
| Quantity Based Discount | 20 + | 25% $29.25 |
What is Semaglutide?
Semaglutide is a synthetic peptide analog of human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), designed to mimic the effects of this naturally occurring incretin hormone. Incretin hormones are a group of metabolic peptides released by the gut in response to food intake—particularly glucose and fat.
The main role of incretin hormones and their analogs, such as semaglutide, is to stimulate insulin secretion from the pancreas in a glucose-dependent manner, meaning they help regulate blood sugar without triggering excessive insulin release when glucose levels are low.
The two primary incretin hormones are:
- GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1)
- GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide)
These hormones support metabolic balance by stimulating insulin secretion, inhibiting glucagon release (which would otherwise raise blood sugar), slowing gastric emptying (to help regulate the pace of digestion), and promoting a feeling of fullness or satiety, which can reduce overall food intake.
Why Use Semaglutide in Your Research?
In research settings, semaglutide is studied for its ability to modulate these mechanisms that are of interest in metabolic and obesity-related studies.
Being a GLP-1 analog, Semaglutide is a modified peptide that includes specific substitutions and a fatty acid side chain, which enhances its binding to albumin and significantly extends its half-life. These modifications make it more stable and resistant to enzymatic degradation compared to native GLP-1, allowing for prolonged activity in vitro and in vivo models.
Researchers value Semaglutide for its:
- High stability under standard storage and handling conditions
- Excellent solubility in common research-grade diluents
- Consistency across experiments due to its chemical design and long half-life
Studies have shown that Semaglutide demonstrates strong GLP-1 receptor agonism, supporting its relevance in research focused on glucose homeostasis, appetite regulation, and weight management pathways.
Important: This product is offered strictly for research use only. It is not approved by the FDA for human or veterinary use. It must not be used for any form of clinical or diagnostic application.
Semaglutide Mechanism of Action (Based on Research)
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, which means it binds to and activates the same receptor that natural GLP-1 does. However, unlike endogenous GLP-1, which breaks down rapidly in the body, Semaglutide has been chemically modified to be long-acting and resistant to enzymatic degradation.
In research, Semaglutide mimics and amplifies the actions of GLP-1, making it especially relevant in studies focused on:
- Glucose regulation
- Appetite control and energy balance
- Obesity and metabolic disorders
The effects of semaglutide have been observed across multiple metabolic and hormonal pathways in preclinical and non-clinical studies. The primary mechanisms involve the following:
Appetite Regulation
Semaglutide has been shown to influence appetite control centers in the brain, particularly within the hypothalamus. Research suggests it may reduce food intake by enhancing satiety signals and lowering hunger levels through GLP-1 receptor activity in the central nervous system (CNS).
In rodent models, chronic administration led to significant decreases in caloric intake and body weight without signs of tolerance development.
Functional MRI data show that Semaglutide alters activation in brain regions involved in reward and motivation, including the insula, putamen, and orbitofrontal cortex, which are associated with food cue reactivity and cravings.
Participants exhibited reduced neural response to high-calorie food images, suggesting a shift in food-related attention and motivation—mechanisms that may contribute to sustained appetite suppression and reduced caloric intake in research contexts.
Blood Sugar Modulation
Semaglutide enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion and suppresses glucagon release, both of which contribute to improved glycemic control in research settings. These actions support a more stable postprandial (after-meal) blood glucose profile.
Importantly, the semaglutide peptide does not typically stimulate insulin when blood glucose is low, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia in research models.
In addition to its pancreatic effects, Semaglutide has been shown to improve the efficiency of glucose disposal in peripheral tissues, enhancing overall glycemic regulation in experimental systems.
Studies suggest that semaglutide helps lower both fasting and postprandial glucose levels by improving insulin sensitivity, reducing hepatic glucose output, and delaying gastric emptying, which collectively help flatten glucose spikes after meals. These mechanisms make it particularly relevant in research focused on insulin resistance, beta-cell function, and type 2 diabetes modeling.
Hormonal Pathways
GLP-1 receptor activation also affects broader hormonal networks. Semaglutide has been observed to slow gastric emptying, influencing gut-brain signaling and the timing of nutrient absorption. These effects are tied to changes in gut-derived hormones, which may further modulate insulin dynamics, satiety, and energy balance.
Recent findings also suggest that Semaglutide may influence neuroendocrine circuits involved in food-related stress regulation and energy homeostasis.
Studies have observed interactions between GLP-1 receptor pathways and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, hinting at potential roles in modulating cortisol levels, feeding behavior under stress, and central energy-sensing mechanisms.
While these findings are still under investigation, they point to Semaglutide’s broader relevance in endocrine-focused research beyond metabolic control alone.
Research Applications (Semaglutide Benefits)
Semaglutide has been the subject of a wide range of non-clinical and preclinical studies exploring its effects on energy regulation, glucose metabolism, and hormonal pathways. As a GLP-1 receptor agonist with enhanced stability and bioavailability, it has become a valuable tool in controlled research environments.
Below are key areas where Semaglutide has been investigated:
Weight Management
Semaglutide has been widely studied for its role in body weight regulation, especially in the context of appetite modulation and caloric intake reduction. In various non-clinical models, including rodent and primate studies, semaglutide peptide has been observed to reduce body weight through mechanisms involving central satiety pathways and food-motivated behavior.
One comprehensive study on this mode is The STEP 1 trial, a randomized, double-blind study published in The New England Journal of Medicine. Participants receiving 2.4 mg of Semaglutide weekly, alongside lifestyle modifications, experienced an average 14.9% reduction in body weight over 68 weeks—substantially more than the placebo group.
These reductions were attributed primarily to decreased appetite, lower food cravings, and reduced energy intake, aligning with earlier findings in animal models.
Important: Although the study involved human subjects, its outcomes are not intended to imply any therapeutic claims. The study provided insight into how Semaglutide influences energy balance in controlled conditions.
A related study published in Nature Metabolism further supported these observations. The research showed that Semaglutide influences not only homeostatic hunger circuits but also hedonic pathways associated with reward-based eating.
Functional MRI data revealed decreased activity in brain regions tied to high-calorie food stimuli, reinforcing the idea that Semaglutide may alter both physiological hunger and food-related motivation.
Together, these findings suggest that Semaglutide’s ability to engage central appetite-regulating networks—particularly in the hypothalamus, brainstem, and reward centers—makes it a valuable compound for ongoing research into obesity, energy regulation, and neuroendocrine control of eating behavior.
Metabolic Studies
Semaglutide is frequently used in metabolic research to investigate glucose homeostasis, insulin dynamics, and lipid metabolism. Its ability to enhance glucose-dependent insulin secretion while suppressing glucagon release makes it particularly relevant in models of type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance.
In particular, research has highlighted improvements in postprandial glucose control, hepatic glucose output, and peripheral glucose uptake—key endpoints in studies of metabolic disease progression.
In one trial, subjects with type 2 diabetes who were administered Semaglutide experienced significant reductions in fasting plasma glucose, postprandial glucose excursions, and mean glucose levels compared to placebo.
The same study also showed that Semaglutide markedly reduced glucose area under the curve (AUC) over a standardized meal test, highlighting its ability to improve glycemic response through coordinated pancreatic and gastrointestinal effects. These findings further underscore its utility as a research agent for exploring both acute and long-term glucose regulation.
Hormonal Research
Beyond glucose and appetite pathways, Semaglutide has been studied for its impact on neuroendocrine signaling. It may influence the gut-brain axis, HPA (hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal) axis, and broader hormonal loops involved in energy balance and stress response.
Emerging evidence points to its effects on thyroid hormone pathways. In rodent models, Semaglutide has been shown to activate GLP-1 receptors in the hypothalamus, indirectly affecting TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) levels and downstream thyroid hormone regulation.
These findings suggest relevance in research beyond metabolism alone, particularly in exploring endocrine feedback mechanisms.
Semaglutide Peptide Characteristics
- Molecular Formula: C₁₈₇H₂₉₁N₄₅O₅₉
- CAS Number: 910463-68-2
- Amino Acid Sequence: HAEGTFTSDVSSYLEGQAAKEFIAWLVRGRG
(Note: Sequence includes chemical modifications to enhance half-life and receptor binding)
- Synonyms: GLP-1(7-37) analog, NN9535,Molar Mass: ~4113.58 g/mol
- Recommended Storage:
- Lyophilized powder: Store at -20°C or lower for long-term stability
- Reconstituted solution: Store at 2–8°C for 30-60 days. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles and exposure to strong light.
| Note: For research use only. Not for human or veterinary use. |
Semaglutide vs Tirzepatide vs Retatrutide (Comparison)
The landscape of GLP-1–based therapies continues to evolve rapidly, with each new compound building upon the mechanisms of its predecessors.
Here’s how the three leading incretin-based compounds compare in terms of structure, function, and research progress:
| Feature | Semaglutide | Tirzepatide | Retatrutide |
| Type | Single agonist (GLP-1) | Dual agonist (GLP-1, GIP) | Triple agonist (GLP-1, GIP, Glucagon) |
| Targets | Appetite suppression, blood sugar control | Appetite suppression, blood sugar control | Appetite suppression, blood sugar control, energy expenditure |
| Mechanism Complexity | Simplest (single pathway) | Moderate (dual pathways) | Most complex (triple pathways) |
| Research Stage | FDA Approved | FDA Approved | Early-stage trials (preclinical and phase 1) |
| Weight Loss Potential (Research) | High — clinically validated | Very high — clinically validated | Potentially highest — based on early data |
| Impact on Glucose Regulation | Strong | Strong | Strong — promising in early studies |
| Additional Effects | Cardiovascular benefits (documented in trials) | Enhanced insulin sensitivity | Increased energy expenditure (in animal studies) |
| Dosing Frequency | Weekly injection | Weekly injection | TBD — under investigation |
| Approval Status | Approved prescription medication under certain brand names | Approved prescription medication under certain brand names | Research use only |
| Disclaimer | Compounded semaglutide is not approved for human use; research only | Compounded semaglutide is not approved for human use; research only | Not approved for human use; research only |
Semaglutide Safety and Side Effects in Studies
Semaglutide is generally well-tolerated, but side effects in studies of human use are common, especially during dose escalation. The most frequently reported include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation.
These gastrointestinal effects are typically mild to moderate and tend to subside over time. Rare but serious risks include pancreatitis and potential thyroid C-cell tumors, though the latter has been observed primarily in rodent studies. It should be noted that many of these side effects apply to other GLP-1 receptor agonists as well.
On the bright side, semaglutide also carries cardiovascular benefits, with studies showing a reduced risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes.
These effects are not yet fully understood, and current findings remain preliminary. Semaglutide peptides are strictly intended for research use only and are not approved for human or veterinary applications.
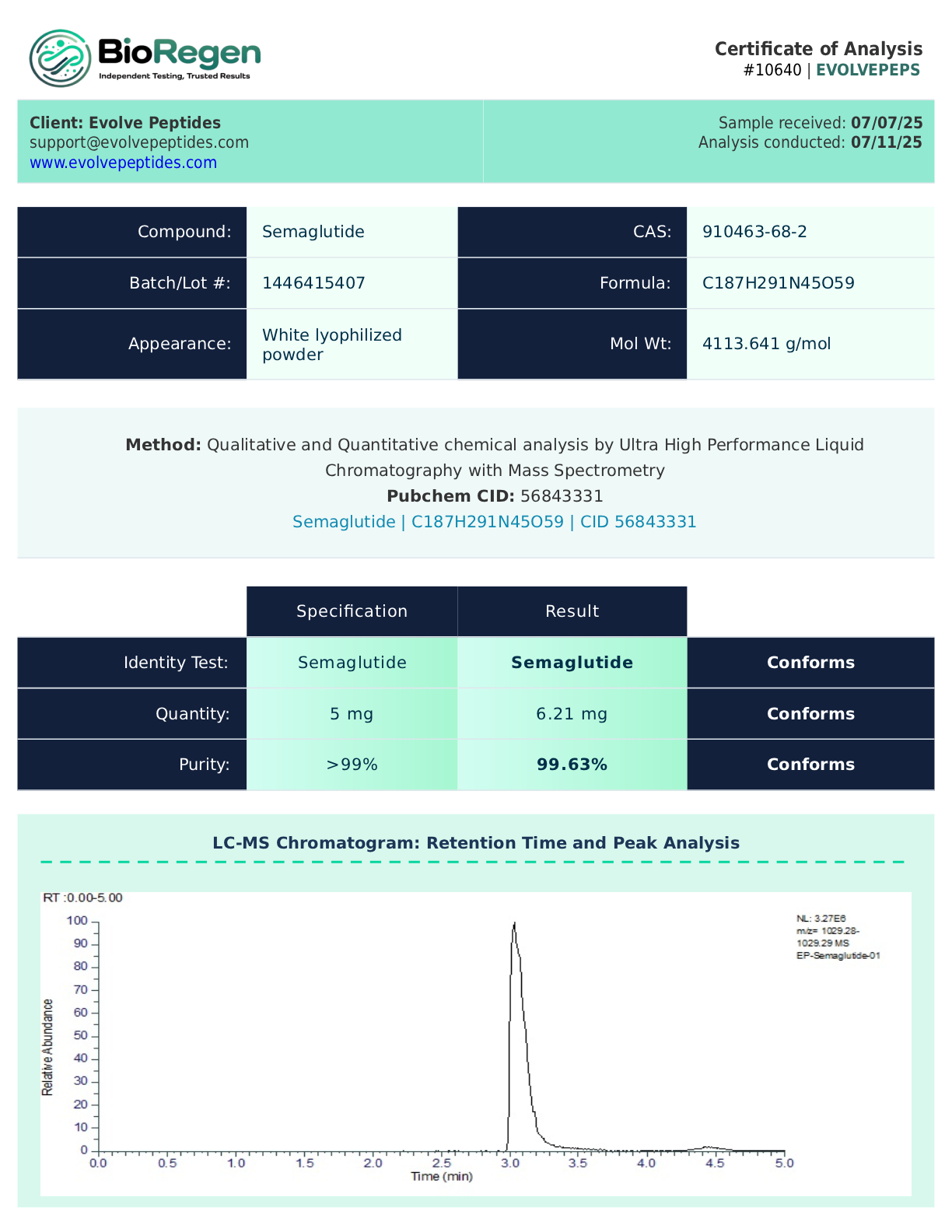
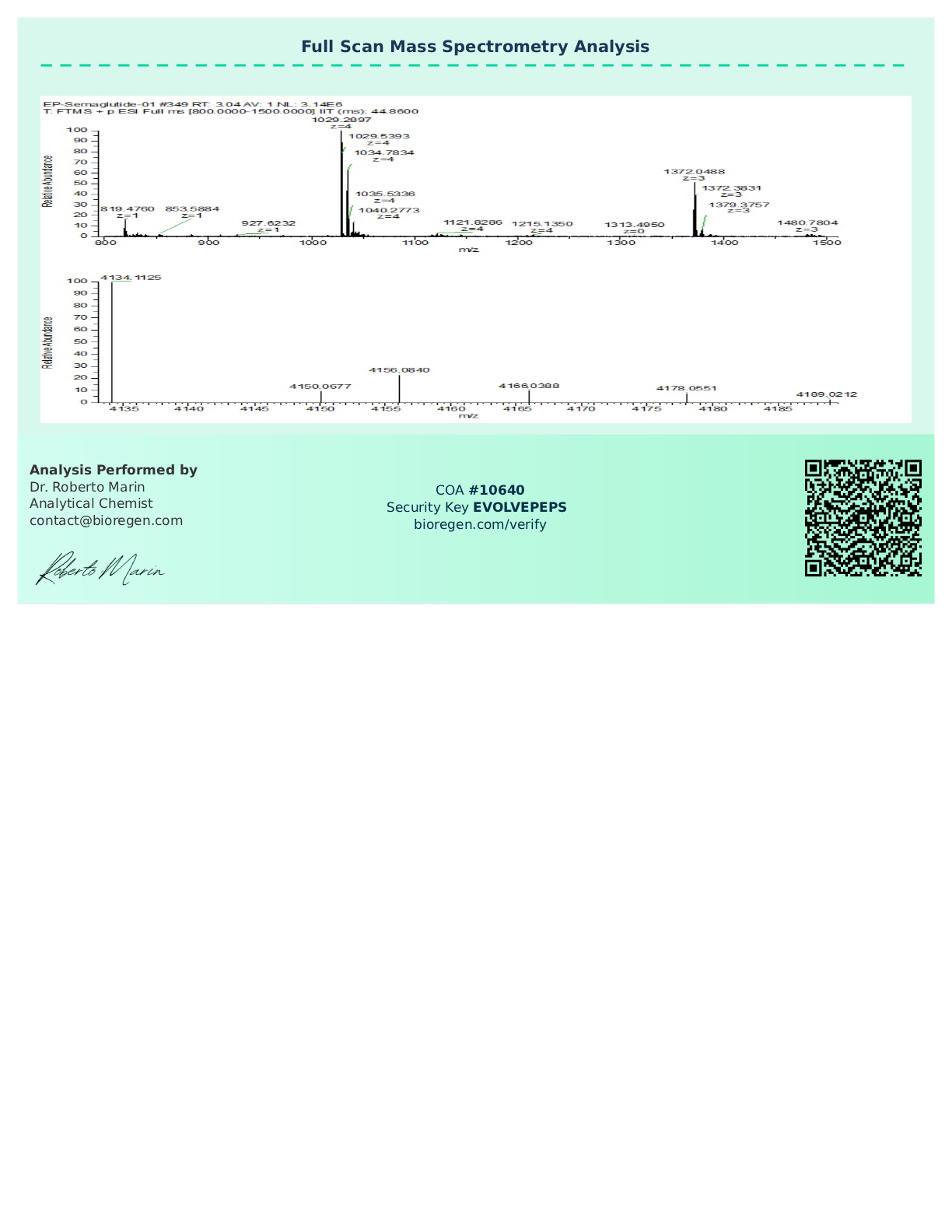
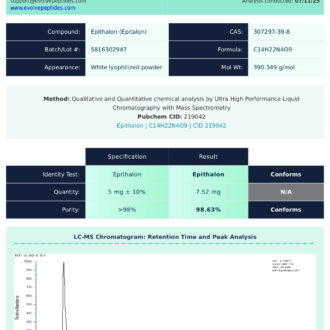
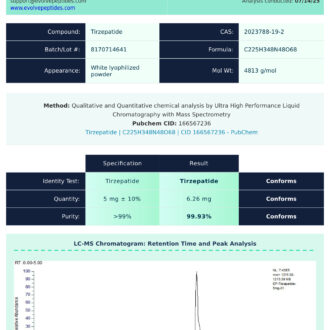
Certificate of Analysis (COA)
All Semaglutide peptide batches offered by Evolve Peptides undergo rigorous third-party testing to confirm identity, purity, and consistency. A Certificate of Analysis (COA) is available for each lot, providing detailed results from independent analytical labs.
Researchers may request a copy of the COA by contacting our support team, or by referencing the batch number included with each order. COAs include test results for purity (HPLC), mass spectrometry, and microbial screening, ensuring confidence in the quality of each vial.
Sample COAs may be made available for review upon request.
Disclaimer
This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only and is not approved for human or veterinary use.
References
- Areesha Moiz, Kristian B. Filion, Michael A. Tsoukas, Oriana HY. Yu, Tricia M. Peters, Mark J. Eisenberg. Mechanisms of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist-Induced Weight Loss: A Review of Central and Peripheral Pathways in Appetite and Energy Regulation. The American Journal of Medicine, 2025. ISSN 0002-9343.
https://www.amjmed.com/article/S0002-9343(25)00059-2/fulltext - Gabery, S., Salinas, C. G., Paulsen, S. J., Ahnfelt-Rønne, M. S., Alanentalo, T., Ma, X., … & Nygaard, E. B. (2020). Semaglutide lowers body weight in rodents via distributed neural pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(11), 4020. https://insight.jci.org/articles/view/133429
- Papakonstantinou, I., Tsioufis, K., & Katsi, V. (2024). Spotlight on the Mechanism of Action of Semaglutide. 46(12), 14514–14541.
https://www.mdpi.com/1467-3045/46/12/872 - Mahapatra, M. K., Karuppasamy, M., & Sahoo, B. M. (2022). Semaglutide, a glucagon like peptide-1 receptor agonist with cardiovascular benefits for management of type 2 diabetes. Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders, 7;23(3):521–539.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00424-024-03047-3 - Hankir, M. K., & Lutz, T. A. (2025). Novel neural pathways targeted by GLP-1R agonists and bariatric surgery. Pflügers Archiv – European Journal of Physiology, 477, 171–185. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00424-024-03047-3
- Wilding, J. P. H., Batterham, R. L., Calanna, S., Davies, M., Hollander, P., Lingvay, I., … & Rubino, D. (2021). Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. The New England Journal of Medicine, 384(11), 989–1002. https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2032183
- Friedrichsen, M., Breitschaft, A., Tadayon, S., Wizert, A., & Skovgaard, D. (2021). The effect of semaglutide 2.4 mg once weekly on energy intake, appetite, control of eating, food preference, and body weight in adults with obesity. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 23(3), 754–762.
https://dom-pubs.pericles-prod.literatumonline.com/doi/10.1111/dom.14280 - Hjerpsted, J. B., Flint, A., Brooks, A., Axelsen, M. B., Kvist, T., & Blundell, J. (2018). Semaglutide improves postprandial glucose and lipid metabolism, and delays first-hour gastric emptying in subjects with obesity. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 20(3), 610–619. https://dom-pubs.pericles-prod.literatumonline.com/doi/10.1111/dom.13120
- Diz-Chaves, Y., Herrera-Pérez, S., González-Matías, L. C., Lamas, J. A., & Mallo, F. (2020). Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) in the Integration of Neural and Endocrine Responses to Stress. Nutrients. 2020 Oct 28;12(11):3304.
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/12/11/3304 - National Center for Biotechnology Information. (n.d.). Semaglutide. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 56843331. Retrieved from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Semaglutide
- Wilding, J. P. H., Batterham, R. L., Calanna, S., Davies, M., Hollander, P., Lingvay, I., … & Rubino, D. (2021). Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. The New England Journal of Medicine, 384(11), 989–1002. https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2032183
- Wan, J., Ferrari, C., & Tadros, M. GLP-1RA Essentials in Gastroenterology: Side Effect Management, Precautions for Endoscopy and Applications for Gastrointestinal Disease Treatment. Gastroenterol. Insights 2024, 15(1), 191-212; https://www.mdpi.com/2036-7422/15/1/14
- European Association for the Study of Obesity. (2025, May 12). Early cardiovascular benefits of semaglutide seen within months in SELECT trial. News-Medical.net. Retrieved from http://www.news-medical.net/news/20250512/Early-cardiovascular-benefits-of-semaglutide-seen-within-months-in-SELECT-trial.aspx
- Areesha Moiz, Kristian B. Filion, Michael A. Tsoukas, Oriana HY. Yu, Tricia M. Peters, Mark J. Eisenberg. Mechanisms of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist-Induced Weight Loss: A Review of Central and Peripheral Pathways in Appetite and Energy Regulation. The American Journal of Medicine, 2025. ISSN 0002-9343.
Contents: 2 mg lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder provided in a 3 ml vial, sealed and sterile. Purity exceeds 99%, guaranteed.
Notes: Requires reconstitution with bacteriostatic water. (Sold Here: BAC Water.)
Application: Potential research application in weight loss studies, particularly obesity.
Chemical Formula: C187H291N45O59
PubChem CID: 139600673
CAS Number: 910463-68-2
Molecular Weight: 4113.8 g/mol
Storage: Store at ≤8°C, sealed, away from heat, light, and moisture. The colder the better.
Purity: >99%
Orders placed before 1 PM EST ship same day.
We use USPS for most of our deliveries. You can expect your parcel within 2-5 business days from when it leaves our warehouse.
Why Choose Us?
Potency & Purity Guaranteed
Our peptides are custom-manufactured to exact specifications. Strictly no compromises.
Rigorously Third-Party Tested
Every product page includes independent lab test results for every peptide we sell.
Dedicated End-to-End Support
We're here for you every step of the way. Our goal is your success in research.
100% Satisfaction Guaranteed
If you are not 100% satisfied with our research peptides, we'll refund everything you paid.